Staphylococcus aureus
-Etymology
:
Staph :
Greek word Meaning “ Grape like cluster”
Coccus : berry (spherical
shape)
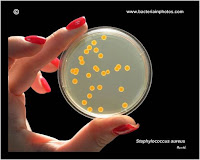
aureus : Latin word
meaning “ Golden” (gives golden yellow color colonies )
-
Discovery
S. aureus was discovered by
the surgeon Sir Alexander Ogston (1880), Scotland in pus from surgical
abscesses
-Habitat: Ubiquitous in nature and normal inhabitant
of the skin and nose( mucous membranes ) of health
persons. S. aureus is infectious to both animals and humans
and may only survive on dry skin. Spread through contaminated
surfaces, air and people.
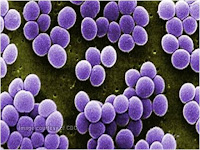
Morphology
-Gram Positive Organism
- Cocci - O - in shape
- Size : 1 to 2 μm in diameter
- Non- motile
- Non- Spore forming
- Appear
in single, pair and short chains
- Some
are have capsule.
Cultural
characteristics
- -Grow on
ordinary medium eg. nutrient agar
- - Growth
temperature is 10 ° C - 42° C
- - Optimum temperature
is 37°C
- - Aerobes and
facultative anaerobes
- - pH range
7.4 to 7.6
- -Nutrient
agar : It produces Circular, smooth, Convex and
opaque colonies.
- - Blood agar : It
produces marked hemolytic (β- hemolysis) colony. (Sheep blood)
- -Mannitol
Salt agar (MSA) : It produce yellow
colonies with yellow zones, whereas other Staphylococci produce pink
or red colonies without color change of the medium
- -Liquid
medium : Uniform
turbidity
- -Selective medium: Salt milk
 |
| Nutrient Agar |
 |
| Blood Agar |
 |
| Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) |
 |
| Salt Milk Agar |
Catalase Test: Positive
Coagulase Test: Positive
Coagulase is an enzyme-like protein and causes plasma to clot
by converting fibrinogen to fibrin in palsma.
Carbohydrate fermentation : S. aureus ferment
mostly mannitol sugar and produce acid
without gas.
Pathogenicity
Infections & Diseases
Skin & Soft Tissue: Boils, Abscess, Wound infection,
Impetigo, Cellulitis, Folliculitis
Musculoskeletal: Osteomyelitis, Arthritis, Pyomyositis
Respiratory: Tonsillitis,
Pharyngitis, Sinusitis, and Bronchopneumonia
Central nervous system: meningitis, abscess
Endovascular: Bactremia, Septcemia, Endocarditis
Urinary Tract Infection : Uncommon
TSS: Toxic Shock Syndrome (Multisystem disease) symptoms are Fever,
Vomiting, Diarrhea, Rashes
SSSS: Staphylococcal Scaled Skin Syndrome is Outer layer of epidermis get separated.
Virulence Factors
Cell surface proteins:
Protein
A:
Anti- phagocycotic, Anti- complimentary and damages the platelets.
Clumping factor: in slide test coagulate the plasma
Extra
Cellular Enzymes:
Lipases (Hydrolysis the lipids),
Hyaluronidases (Breakdown the Hyaluronic
acid present in the
tissues),
Nucleases (Breakdown nucleic acid)
Toxins: Cytolytic cytotoxins;
hmolysins ,
Leucocidine
Enterotoxin:
Causes Staphylococcus food poisoning
Types are A, B, C1-3,
D, E & F
Present
in Mil products, meat etc.,
Laboratory Diagnosis
Collection
of Samples: Skin Scrapping, Pus, Food
samples, Throat and nasal swabs.
Microscopic
observation: Gram staining
Culture:
Nutrient agar, Blood agar, Mannitol Salt agar (MSA)
Biochemical
Test: Catalase Test,
Coagulase Tests (Slide and
Tube Test)
Antibiotic
Sensitivity Test ( Kirby bauer Method )
:
Drugs : Penicillin,
Methicillin (Some strains are resistant
against Methicillin are called MRSA)
Coaxacillin,
Bacitracin, Vancomycin, Rifampicin, Cephalosporins ,
Erythromycin, Tetracyclines etc.
Other diagnosis methods:
Phage Typing: Phage typing is a method used for detecting single strains of
bacteria. It is used to trace the source of outbreaks of infections. The
viruses that infect bacteria are called bacteriophages.
Molecular Typing : Using RFLP,
RAPD, MLST ,
MALDI-TOF:
emerging technique to identify the
unkown bacteria

No comments:
Post a Comment