NOTIFICATIONS
Wednesday, June 27, 2018
Provisional/Permanent registration, Statutory Licenses
| Registration / Statutory Licenses And Clearances: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Provisional (temporary) Registration : | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Monday, June 25, 2018
16th IAAM National Conference Brochure & Registration form
16th IAAM National Conference On
"Human Microbiome InPersonal Medicne- Bridging Human & Microbes for Future Sustainability"
By
JSS Acadmy of Higher Education Research
&
Indian Association of Applied Microbiologists (IAAM)
Click the following links for Brochure and Registration form :
Preparation of Project report
Project Report is a written document relating to any investment. It contains data on the basis of which the project has been appraised and found feasible. It consists of information on economic, technical, financial, managerial and production aspects. It enables the entrepreneur to know the inputs and helps him to obtain loans from banks or financial Institutions.
The project report contains detailed information about Land and buildings required, Manufacturing Capacity per annum, Manufacturing Process, Machinery & equipment along with their prices and specifications, Requirements of raw materials, Requirements of Power & Water, Manpower needs, Marketing Cost of the project, production, financial analyses and economic viability of the project.
Contents of a Project Report
Following are the contents of a project report.
1. General Information
A project report must provide information about the details of the industry to which the project belongs to. It must give information about the past experience, present status, problems and future prospects of the industry. It must give information about the product to be manufactured and the reasons for selecting the product if the proposed business is a manufacturing unit. It must spell out the demand for the product in the local, national and the global market. It should clearly identify the alternatives of business and should clarify the reasons for starting the business.
2. Executive Summary
A project report must state the objectives of the business and the methods through which the business can attain success. The overall picture of the business with regard to capital, operations, methods of functioning and execution of the business must be stated in the project report. It must mention the assumptions and the risks generally involved in the business.
3. Organization Summary
The project report should indicate the organization structure and pattern proposed for the unit. It must state whether the ownership is based on sole proprietorship, partnership or joint stock company. It must provide information about the bio data of the promoters including financial soundness. The name, address, age qualification and experience of the proprietors or promoters of the proposed business must be stated in the project report.
4. Project Description
A brief description of the project must be stated and must give details about the following:
- Location of the site,
- Raw material requirements,
- Target of production,
- Area required for the workshed,
- Power requirements,
- Fuel requirements,
- Water requirements,
- Employment requirements of skilled and unskilled labour,
- Technology selected for the project,
- Production process,
- Projected production volumes, unit prices,
- Pollution treatment plants required.
If the business is service oriented, then it must state the type of services rendered to customers. It should state the method of providing service to customers in detail.
5. Marketing Plan
The project report must clearly state the total expected demand for the product. It must state the price at which the product can be sold in the market. It must also mention the strategies to be employed to capture the market. If any, after sale service is provided that must also be stated in the project. It must describe the mode of distribution of the product from the production unit to the market. Project report must state the following:
- Type of customers,
- Target markets,
- Nature of market,
- Market segmentation,
- Future prospects of the market,
- Sales objectives,
- Marketing Cost of the project,
- Market share of proposed venture,
- Demand for the product in the local, national and the global market,
- It must indicate potential users of products and distribution channels to be used for distributing the product.
6. Capital Structure and operating cost
The project report must describe the total capital requirements of the project. It must state the source of finance, it must also indicate the extent of owners funds and borrowed funds. Working capital requirements must be stated and the source of supply should also be indicated in the project. Estimate of total project cost, must be broken down into land, construction of buildings and civil works, plant and machinery, miscellaneous fixed assets, preliminary and preoperative expenses and working capital.
Proposed financial structure of venture must indicate the expected sources and terms of equity and debt financing. This section must also spell out the operating cost
7. Management Plan
The project report should state the following.
- Business experience of the promoters of the business,
- Details about the management team,
- Duties and responsibilities of team members,
- Current personnel needs of the organization,
- Methods of managing the business,
- Plans for hiring and training personnel,
- Programmes and policies of the management.
8. Financial Aspects
In order to judge the profitability of the business a projected profit and loss account and balance sheet must be presented in the project report. It must show the estimated sales revenue, cost of production, gross profit and net profit likely to be earned by the proposed unit. In addition to the above, a projected balance sheet, cash flow statement and funds flow statement must be prepared every year and at least for a period of 3 to 5 years.
The income statement and cash flow projections should include a three-year summary, detail by month for the first year, and detail by quarter for the second and third years. Break even point and rate of return on investment must be stated in the project report. The accounting system and the inventory control system will be used is generally addressed in this section of the project report. The project report must state whether the business is financially and economically viable.
9. Technical Aspects
Project report provides information about the technology and technical aspects of a project. It covers information on Technology selected for the project, Production process, capacity of machinery, pollution control plants etc.
10. Project Implementation
Every proposed business unit must draw a time table for the project. It must indicate the time within the activities involved in establishing the enterprise can be completed. Implementation schemes show the timetable envisaged for project preparation and completion.
11. Social responsibility
The proposed units draws inputs from the society. Hence its contribution to the society in the form of employment, income, exports and infrastructure. The output of the business must be indicated in the project report.
Source: https://accountlearning.com/project-report-meaning-contents-project-report/
Friday, June 15, 2018
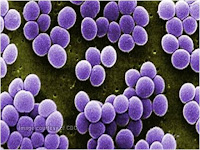
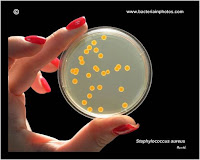
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus
-Etymology
:
Staph :
Greek word Meaning “ Grape like cluster”
Coccus : berry (spherical
shape)
aureus : Latin word
meaning “ Golden” (gives golden yellow color colonies )
-
Discovery
S. aureus was discovered by
the surgeon Sir Alexander Ogston (1880), Scotland in pus from surgical
abscesses
-Habitat: Ubiquitous in nature and normal inhabitant
of the skin and nose( mucous membranes ) of health
persons. S. aureus is infectious to both animals and humans
and may only survive on dry skin. Spread through contaminated
surfaces, air and people.
Morphology
-Gram Positive Organism
- Cocci - O - in shape
- Size : 1 to 2 μm in diameter
- Non- motile
- Non- Spore forming
- Appear
in single, pair and short chains
- Some
are have capsule.
Cultural
characteristics
- -Grow on
ordinary medium eg. nutrient agar
- - Growth
temperature is 10 ° C - 42° C
- - Optimum temperature
is 37°C
- - Aerobes and
facultative anaerobes
- - pH range
7.4 to 7.6
- -Nutrient
agar : It produces Circular, smooth, Convex and
opaque colonies.
- - Blood agar : It
produces marked hemolytic (β- hemolysis) colony. (Sheep blood)
- -Mannitol
Salt agar (MSA) : It produce yellow
colonies with yellow zones, whereas other Staphylococci produce pink
or red colonies without color change of the medium
- -Liquid
medium : Uniform
turbidity
- -Selective medium: Salt milk
 |
| Nutrient Agar |
 |
| Blood Agar |
 |
| Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) |
 |
| Salt Milk Agar |
Catalase Test: Positive
Coagulase Test: Positive
Coagulase is an enzyme-like protein and causes plasma to clot
by converting fibrinogen to fibrin in palsma.
Carbohydrate fermentation : S. aureus ferment
mostly mannitol sugar and produce acid
without gas.
Pathogenicity
Infections & Diseases
Skin & Soft Tissue: Boils, Abscess, Wound infection,
Impetigo, Cellulitis, Folliculitis
Musculoskeletal: Osteomyelitis, Arthritis, Pyomyositis
Respiratory: Tonsillitis,
Pharyngitis, Sinusitis, and Bronchopneumonia
Central nervous system: meningitis, abscess
Endovascular: Bactremia, Septcemia, Endocarditis
Urinary Tract Infection : Uncommon
TSS: Toxic Shock Syndrome (Multisystem disease) symptoms are Fever,
Vomiting, Diarrhea, Rashes
SSSS: Staphylococcal Scaled Skin Syndrome is Outer layer of epidermis get separated.
Virulence Factors
Cell surface proteins:
Protein
A:
Anti- phagocycotic, Anti- complimentary and damages the platelets.
Clumping factor: in slide test coagulate the plasma
Extra
Cellular Enzymes:
Lipases (Hydrolysis the lipids),
Hyaluronidases (Breakdown the Hyaluronic
acid present in the
tissues),
Nucleases (Breakdown nucleic acid)
Toxins: Cytolytic cytotoxins;
hmolysins ,
Leucocidine
Enterotoxin:
Causes Staphylococcus food poisoning
Types are A, B, C1-3,
D, E & F
Present
in Mil products, meat etc.,
Laboratory Diagnosis
Collection
of Samples: Skin Scrapping, Pus, Food
samples, Throat and nasal swabs.
Microscopic
observation: Gram staining
Culture:
Nutrient agar, Blood agar, Mannitol Salt agar (MSA)
Biochemical
Test: Catalase Test,
Coagulase Tests (Slide and
Tube Test)
Antibiotic
Sensitivity Test ( Kirby bauer Method )
:
Drugs : Penicillin,
Methicillin (Some strains are resistant
against Methicillin are called MRSA)
Coaxacillin,
Bacitracin, Vancomycin, Rifampicin, Cephalosporins ,
Erythromycin, Tetracyclines etc.
Other diagnosis methods:
Phage Typing: Phage typing is a method used for detecting single strains of
bacteria. It is used to trace the source of outbreaks of infections. The
viruses that infect bacteria are called bacteriophages.
Molecular Typing : Using RFLP,
RAPD, MLST ,
MALDI-TOF:
emerging technique to identify the
unkown bacteria
Friday, June 8, 2018
Role of Entrepreneurs
1. Employment opportunities
Entrepreneurs employ labour for managing their business activities and provides employment opportunities to a large number of people. They remove unemployment problem.
2. Balanced Regional Development
Government promotes decentralized development of industries as most of the incentives are granted for establishing industries in backward and rural areas. Thus, the entrepreneurs to avail the benefits establish industries in backward and rural areas.
They remove regional disparities and bring balanced regional development. They also help to reduce the problems of congestion, slums, sanitation and pollution in cities by providing employment and income to people living in rural areas. They help in improving the standard of living of the people residing in suburban and rural areas.
3. Mobilization Of Local Resources
Entrepreneurs help to mobilize and utilize local resources like small savings and talents of relatives and friends, which might otherwise remain idle and unutilized. Thus they help in effective utilization of resources.
4. Optimization Of Capital
Entrepreneurs aim to get quick return on investment. They act as a stabilizing force by providing high output capital ratio as well as high employment capital ratio.
5. Promotion of Exports
Entrepreneurs reduce the pressure on the country’s balance of payments by exporting their goods they earn valuable foreign exchange through exports.
6. Consumer Demands
Entrepreneurs produce a wide range of products required by consumers. They meet the demand of the consumers without creating a shortage for goods.
7. Social Advantage
Entrepreneurs help in the development of the society by providing employment to people and paves for independent living They encourage democracy and self-governance. They are adept in distributing national income in more efficient and equitable manner among the various participants of the society.
8. Increase per capita income
Entrepreneurs help to increase the per capita income of the country in various ways and facilitate development of backward areas and weaker sections of the society.
9. Capital formation
A country can attain economic development only when there is more amount of investment and production. Entrepreneurs help in channelizing their savings and savings of the public to productive resources by establishing enterprises. They promote capital formation by channelizing the savings of public to productive resources.
10. Growth of capital market
Entrepreneurs raises money for running their business through shares and debentures. Trading of shares and debentures by the public with the help of financial services sector leads to capital market growth.
11. Growth of infrastructure
The infrastructure development of any country determines the economic development of a country, Entrepreneurs by establishing their enterprises in rural and backward areas influence the government to develop the infrastructure of those areas.
12. Development of Trader
Entrepreneurs play an important role in the promotion of domestic trade and foreign trade. They avail assistance from various financial institutions in the form of cash credit, trade credit, overdraft, short term loans, secured loans and unsecured loans and lead to the development of the trade in the country.
13. Economic Integration
Entrepreneur reduces the concentration of power in a few hands by creating employment opportunities and through equitable distribution of income. Entrepreneurs promote economic integration in the country by adopting certain economic policies and laws framed by the government. They help in removing the disparity between the rich and the poor by adopting the rules and regulation framed by the government for the effective functioning of business in the country.
14. Inflow of Foreign Capital
Entrepreneurs help to attract funds from individuals and institutions residing in foreign countries for their businesses.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
