Acid
Fast Stain (Ziehl- Neelsen Method)
Aim:
To perform acid fast staining to identify Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium leprae.
Introduction :
The
Ziehl Neelsen Method is used for staining Mycobacterium
sp. in clinical specimens. The thick outer waxy covering (mycolic acid) of the
Mycobacterium cell walls act as a barrier and does not allow all the
stains to enter into the cell. In order to visualize these cells higher
concentrations of the staining solution is needed and once this stain enters
the cell, it is too difficult to remove the stain using a decolorizer. When the
clinical specimen is stained with basic dyes such as carbol fuchsin (primary
stain) with the continuous application of heat, softens the waxy lipid outer
covering of the cell wall and the stain readily enters the cell and stains the
cell cytoplasm. When decolorizing agents such as acid-alcohol is added over the
primary stain, some bacterial cells cannot be easily decolorized and such
bacterial cells are called as acid fast bacteria. The bacteria with high
concentration of lipid are easily decolorized by the decolorizing agent and are
said to be non-acid fast bacteria. Finally, the addition of the counter stain,
Methylene blue, dyes the colorless non acid fast cells as blue thus
differentiating them from the pink acid fast bacteria which are unaffected by
the Methylene blue.
Materials
Required:
1. A clean grease free slide.
2. A bacterial cell suspension.
3. Staining agent- carbol fucshin.
4. Boiling water bath.
5. Decolourising agent – Acid alcohol
6. Counter stain – 1% Methylene blue
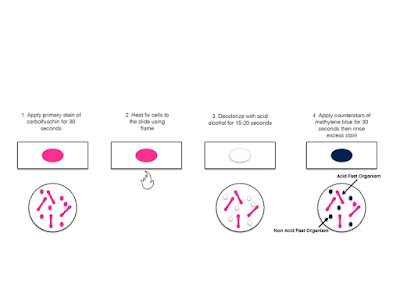
Procedure :
- Smear
of organisms were prepared on clean glass slide
- The
slide was allowed to air dry and heat fixed..
- The
slide was flooded with carbol fucshin stain and placed on a boiling water
bath for steaming for about 3-5 minutes.
- During
steaming the stain is repeatedly added on the slide to avoid drying of
smear.
- Further
the slide was delcolourised with acid alcohol until the stain disappear in
washing.
- After
decolourisation the slide was given a water wash treatment.
- Further
the smear was flooded with the counter stain that is 1% Methylene
blue for about one minute.
- The
slide was then washed with water, air dried and observed under oil
immersion objective.
Result:
On microscopic observation, the acid fast bacterium appeared
as pink coloured cells, non-acid fast cells appeared blue.
Discussion:
Acid fast stain is due to relative solubility of carbol fuchsin
and impermeability of call wall. Fuchsin is more soluble on carbolic acid than
in water and carbolic acid soluble more easily in lipids than in acid alcohol. Therefore
carbol fuchsin has higher affinity for
lipids than acid alcohol and will remain within the cell wall when washed with
decolouriser.

No comments:
Post a Comment